GRS: GLOBAL TEXTILE RECYCLING STANDARD
The Global Recycled Standard (GRS) is a popular international standard, widely applied around the world. Organizations and businesses should learn and apply this standard to keep up with the trend of sustainable production. Compliance with GRS not only helps businesses enhance their reputation but also opens up many opportunities for integration and development in the future.
1. WHAT IS GRS?
GRS stands for Global Recycled Standard, a standard developed by Control Union Certifications in 2008 and transferred to Textile Exchange on January 1, 2011. This standard applies to all textile products made from at least 20% recycled materials, helping to promote the use of recycled materials in production.

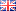
GRS standards for recycled products
The main requirements of the GRS standard include:
– Recycled content requirement: is the most basic principle of the GRS standard. Ensure that the product must contain at least 20% recycled material to contribute to waste reduction and environmental protection.
– Traceability requirement: The entire supply chain of the product must be traceable, helping to prevent the use of recycled materials from unreliable sources
– Responsible production requirement: Production must comply with environmental, social and humanitarian regulations, including the use of energy, water saving, aiming at safety, respect and protection of workers’ health.
– Chemical requirements: Limit the use of toxic chemicals in production to minimize the impact of chemicals on the environment and human health
– Labeling requirements: Products must be clearly labeled with recycled content and other requirements of the GRS standard to help users easily identify products that meet the GRS standard.
2. THE IMPORTANCE OF GRS FOR THE TEXTILE AND GARMENT INDUSTRY
According to the Vietnam Textile and Apparel Association (VITAS), the textile and garment industry spends about 3 billion USD per year on energy consumption and accounts for about 8% of the energy demand of the entire industry, emitting about 5 million tons of CO2 per year. Notably, the fashion industry accounts for about 10% of global carbon emissions, more than the aviation and shipping industries. This shows that the textile and garment industry is facing major environmental challenges.
To address these challenges, textile and garment enterprises are increasingly interested in sustainability standards. GRS standards are an important tool to promote sustainable development in the textile and garment industry, creating a competitive advantage for businesses in the context of the market increasingly prioritizing green products.
2.1. Why is GRS an inevitable standard for the textile industry?
The Global Recycled Standard (GRS) is becoming an inevitable trend in the textile industry, especially when the demand for sustainable production is increasing. Applying GRS brings many practical benefits to textile and garment enterprises, including:
– Enhance product sustainability: GRS helps minimize the negative impact of the textile and garment industry on the environment and society by encouraging the use of recycled materials and improving production processes.
– Enhance the reputation of the enterprise: Achieving GRS standards not only helps enterprises build an environmentally friendly image but also attracts customers interested in sustainable and socially responsible products.
– Market expansion: GRS opens up opportunities to access demanding markets, such as Europe, which have high requirements for sustainability standards and recycled product certification.
2.2. Benefits of GRS standards for businesses
Applying the Global Recycled Standard (GRS) brings many practical benefits to textile and garment businesses, including:
– Enhanced reputation and customer trust: GRS helps businesses affirm their commitment to sustainable development, attracting and retaining customers interested in environmentally friendly products.
– Minimizing legal risks: Complying with GRS standards helps businesses meet environmental and social regulations, thereby reducing the risk of fines or lawsuits.
– Cost savings: Using recycled materials can help businesses reduce production costs while optimizing economic efficiency.
2.3. Textile Industry Trends and GRS Certification
The textile industry is currently one of the largest and most polluting industries globally. According to estimates from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the industry accounts for approximately 10% of carbon emissions and 20% of industrial wastewater worldwide. Increased consumer interest in environmentally friendly products has prompted textile and apparel companies to shift to sustainable production methods.
Sustainability trends in the textile and apparel industry include:
– Using recycled materials: Recycled fabrics from plastic bottles (PET), natural fibers such as cotton, or plant-based fibers such as flax and banana fibers are gaining popularity. This significantly reduces textile waste.
– Water conservation and renewable energy use: New technologies such as waterless dyeing and the use of solar and wind energy in production significantly reduce emissions and water consumption.
– Increased social responsibility: Companies are paying more attention to ensuring good working conditions for workers and avoiding forced labor, thereby enhancing corporate social responsibility.
A report by Custom Market Insights indicates that the sustainable textile market will grow strongly in the coming years, from USD 7.6 billion in 2023 to USD 33.1 billion in 2033, with an annual growth rate of up to 22.9%. These trends reflect the growing demand for fashion and textile products that are sustainably sourced, transparent in supply chains, and produced in an environmentally friendly manner.
2.4. Challenges and opportunities of the textile industry
The textile industry is facing serious challenges but also opens up many opportunities for future development. The Textile Exchange’s “Materials Market Report 2023” shows that the textile industry is one of the most polluting industries in the world, with greenhouse gas emissions accounting for about 7-10% of the global total. The industry also consumes large amounts of water and generates large amounts of solid waste. Furthermore, emissions from this industry come not only from production but also from post-consumer products that are not effectively recycled.
In terms of growth, the global textile consumption rate is expected to slow down slightly in the period 2023-2027, reaching only 2.5% per year, compared to 3.5% in the previous period. This reflects the trend of changing consumer behavior and fierce competition from emerging markets.
However, there are significant opportunities for the industry to become more sustainable. The Asia-Pacific market is expected to account for 60% of global textile and apparel consumption growth by 2027, particularly as emerging markets there are increasingly demanding. In addition, the trend for sustainable consumption is growing, with demand for sustainable fashion products expected to increase by 5.5% per year from 2023 to 2027. New technologies such as 3D printing and advanced textiles are also opening up new potential for the industry, especially in areas such as sportswear, health and wellness.
To seize these opportunities, businesses need to invest in research and development of environmentally friendly production processes, take advantage of new technologies and strengthen cooperation with partners in the supply chain.
Khang Anh Intercom products not only meet GRS standards but also carry a commitment to environmental protection, helping businesses firmly step on the journey of sustainable development and building a green future.

 Eng
Eng